WAEC Past Question For Economics - waec econs past questions & answers
Below Are Economics Past Questions And Further Observations
Question 1: The table below represents a traveler's consumption of bottles of Coca-Cola. Further study the table carefully and answer the questions that follow.
No of bottles Total Utility Marginal Utility
1 15 15
2 29 F
3 42 13
4 D 12
5 65 G
6 75 H
7 E 0
(a) Complete the missing figures D, E, F, G and H.
(b) Draw the demand curve for the traveler's consumption of Coca-Cola.
(The use 01" a graph sheet is essential).
(C) Explain the law of diminishing marginal utility as the basis for the slope ofthe traveller's demand curve.
Observation: Furthermore, a great proportion of the candidates who attempted this question scored 10\\ marks. ['viost A them could not draw the appropriate demand curve as required in the (b) part 01 the question. however, some candidates misplaced the explanation of the law of diminishing marginal utility as required in the (c) part of the question with the law of diminishing marginal returns. In order to score good marks, candidates were expected to present their answers as follow:
1. (b) To draw the demand curve there must be information 011 both quantities and prices. In
equilibrium MU= P, therefore the marginal utility COIUIllIl rcprescru-, prices
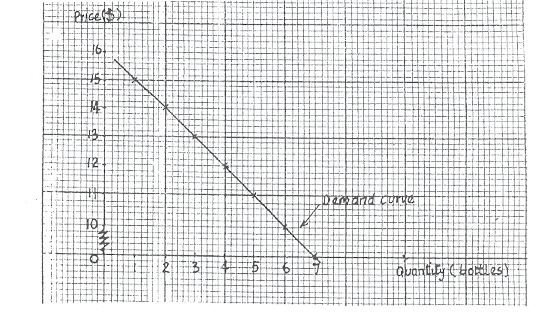
(c) According to the law, marginal utility falls when quantity consumed increases
In equilibrium MU= P. therefore, for MU to Call, price must Call to encourage the consumer to consume more. In other words. it is as price falls that quantity demanded increases as shown in the demand curve
Question 2: Table below represents the cost function of a poultry farm. The price of a crate of egg. is
$21. Use the information contained in the table to answer the questions that follow.
Quantity of eggs(in crates) Total Cost
0 50
1 55
2 62
3 75
4 96
5 125
6 162
7 203
8 248
(a) What is the fixed cost of the farm?
(b) (i) Calculate the marginal cost at each level of output
(ii) What is the profit maximizing output of the farm?
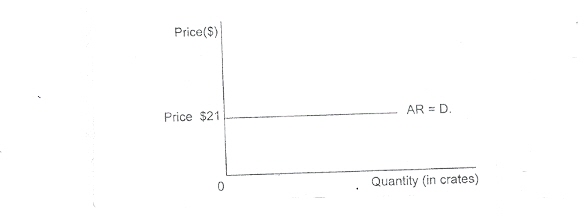
(c) Draw the demand curve for the farm.
Observation: Majority of the candidates who answered this question had no difficulty in providing the correct answers for the (a) and b(i) parts of the question. However, most of' them had difficulties in determining the profit maximizing output and drawing the demand curve of the farm as required in the b( ii) and (e) parts of the question. Candidates needed to present the following answers to score maximum marks for this question.
MC4 = 96-75 = 21 = 21
4-3 1
This where MC output is 4 crates of eggs
(c) D = AR
(AR = $21)
Question 3: With an appropriate illustration, explain the circumstance in which an increase ill output of a producer would
(a) decrease his sales revenue;
(b) increase his sales revenue.
Observation: Most candidates did not attempt this question and the few who did scored very low marks. There is the possibility that most of the candidates were not properly taught the related topics by their teachers. This question required that candidates wrote down the Iullowing details III Score the maximum marks.
(a) An increase in output would decrease the sales revenue of a producer where demand is price inelastic. The explanation is as follows:
(i) An increase in output, given demand, will reduce the price and increase the quantity demanded.
(ii) If demand is price inelastic, the increase in the quality demanded will be proportionately smaller than the reduction in the price.
(iii) Therefore sales revenue will decrease.
Illustration
A 40% fall in price is matched by a 10(1'0 Increase III quantity demanded i.e demand is price inelastic.
Period Price Quantity Demanded Sales Revenue
$ $
I 100 500 50.000
2 60 550 33.000
(b) An increase in output would increase the sales revenue ora producer where the demand for the product is price elastic. The explanation is as follows:
(i) An increase in output given demand will reduce the price and increase tile quantity demanded for the product.
(ii) If demand is price elastic. the increase in the quantity demanded will hl' proportionately greater than the reduction in price.
(ii i) Therefore sales revenue will increase.
Illustration
A 10% fall in price is matched by a 40% Increase in quantity demanded i.e demand is price elastic.
Period Price Quantity Demanded Sales Revenue
$ $
1 100 500 50.000
2 90 700 63.000
Question 4: (a) Define increase in supply.
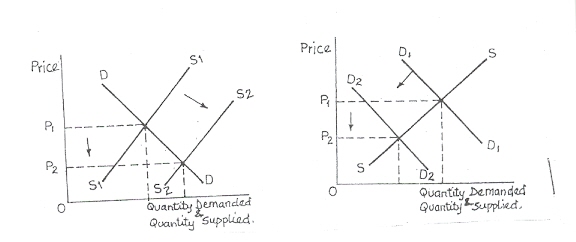
(b) With the aid of diagrams. explain the effect of an increase in the supply of fish on the price of beef.
Observation: 'The (a) part of this question was not difficult for most candidates. they were able to define the increase in supply to a great extent. However, in the (b) part most candidates could not accomplish their explanations with appropriate diagrams as demanded in the question. This fact made them to score average marks. Candidates were expected to present the following to score the optimum marks for this question.
Increase in supply of fish Effects on the price of Beef
Question 5: (a) What is the equilibrium of a consumer?
(b) Explain how a consumer attains equilibrium in spending his income.
Observation: This question was 110 times attempted by most candidates. The few who attempted it scored low marks. This was due to the fact that most of the candidates did not mention the effect ora price rise or fallen equilibrium and how equilibrium could be attained afterwards.
Candidates were expected to state for example.that if' the price or X PX falls. the equilibrium condition would no longer be satisfied. Marginal utility of X. MUx would he greater than the Px i.e. MU > Px.
Furthermore, to establish an equilibrium. MUx must fall to the same level as Px. This happens when the consumer buys more of X. On the other hand. if the Px rises. again the equilibruim condition would not be satisfied. MUx < Px. To attain an equilibrium. the consumer would buy less of X to raise the MUx to the same level as Px.
Question 6: (a) Explain. with examples, the following types of production:
(i) Primary;
(ii) Secondary;
(iii) Tertiary.
(b) Give two reasons why primary production pre-dominates in developing countries.
Observation: The question was very popular among candidates and performance was high and quite encouraging. However, some candidates had difficulty with thetb) pan or the question. they could not give reasons why primary production pre-dominates in developing countries. This led to low scores by candidates in this category. These candidates were expected to write down any two of the following in details:
(i) inadequate capital;
(ii) low technology;
(iii) shortage of relevant skills:
(iv) inadequate infrastructure:
(v) inadequate entrepreneurial capacity:
(vi) small market size:
(vii) lack of research support to push the secondary and tertiary sectors.
Question 7: (a) What is a partnership?
( b) State any two advantages and any two disadvantages of a partncrshship
Observation: A large number of candidates attempted this question and their overall performance was well above average. Almost all the candidates were able to explain what partnership is and stating the advantages and disadvantages of partnership appeared to be no difficulty to them However, very few candidates did not expatiate their points in the (b) part, probably because they assumed the word 'state' in the question meant mere listing of points. These candidates scored low marks for this reason.
Question 8: (a) What is privatization?
(b) Give four reasons far government participation in economic activities in your country
Observation: This question was not very popular with the candidates Most of the candidates who attempted this question gave definitions of privatization which were not appropriate. Candidates answers in the (b) part of this question also fell short of expectation as most candidates could not give correct reasons for government participation in economic activities
However, to score a better mark in this question, candidates were expected to answer it as follows:
(a) Privatization is the transfer to private ownership and control assets or enterprises which
were previously under public ownership.
(b) Reasons for government participation in economic activities include:
(i) To provide necessities
(ii) To make up for inadequate domestic capital
(iii) To establish ideology
(iv) For national sea-preservation
(v) To protect the economy from private monopolies
(vi) To avoid waste through unnecessary competition
(vii) To carry out government policy e.g. the Central Bank.
(viii ) To avoid subsidizing a private enterprise for too long.
(ix) To provide employment.
(x) To provide basic amenities.
(xi) To create wealth for the common good.
(xii) To bring about even development
Question 9: (a) Distinguish between location of industries and localization 01" industries.
(b) Describe any three advantages and any two disadvantages of locating industrics in rural areas.
Observation: The (a) part of this question was popular with the candidates and those who attempted it were able to give appropriate answers. However, the (b) part was poorly attempted. Many candidates provided incoherent answers and failed to expatiate their points which included
Advantages of locatgng industries in the rural areas are:
(i) It checks the drift of young people from the rural areas to the towns and cities.
(ii) Labor is likely to be cheaper in the rural areas.
nbsp; (iii) Transportation and accommodation problems of staff are likely to be less acute.
(iv) The industrial atmosphere would be more peaceful, free from traffic congestion.
(v) Land is likely to be more easily available in the rural areas.
(vi) It will be easier for the firm to get raw materials in the rural areas.
(vii) It would bring about development and improvement in the standard or living in the area.
Advantages of locating industries in the rural areas are:
(i) Basic infrastructure may not be available. The industry may have to provide such infrastructure at its own expense, thus raising the unit cost or production.
(ii) Skilled workers from the urban areas may be unwilling to work in the rural areas. unless they are given substantial incentives.
(iii) There may not be suitable accommodation that could be rented lor use as factories and offices. (iv) The business may have to build its own houses at great expense.
(v) It is more difficult for workers to find alternative employment if they lose their jobs lor one reason or the other.
(vi) Damages and losses may be suffered when moving the goods to the markets in urban areas.
(vii) The market lor finished goods my be small or non-existent in the rural area
Question 10: (a) Explain the function of money as a
(i) measure of value;
(ii) store of value.
(b) Show how inflation affects these two functions of money.
Observation: The question was very popular with the candidates but not well tackled. Majority of the candidates displayed limited knowledge of how inflation could affect the functions of money listed in the (a) part of the question. However, few candidates stated the following to score high marks in the (b) part or the question.
Low inflation affects money as a measure of value
Since inflation reduces the value of money, its function as a measure 01' value is affected. If the inflation is general, prices may rise to the same extent so that relative values or commodities would remain unchanged. On the other hand. il tile inllation affects some commodities more than others then the relative values between commodities would change.
How inflations affects money as a store of value
When there is inflation money loses value. More money is exchanged lor a particular commodity. In other words, a given unit of money exchanges lor less goods. In such circumstances people hesitate to store their wealth in terms or money. The money saved would lose part of its value. It would exchange for less output in future than now. In such circumstances people prefer to save in terms or assets which are likcl, to appreciate
in value like land and buildings.
Question 11: (a) What is a commercial bank?
(b) Describe any four ways by which the Central Bank controls the amount or-credit given by the commercial banks.
Observation: A good number of candidates answered this question. The overall performance was well above average. Candidates were able to state what a commercial bank is and their descriptions of how the Central bank controls the amount or credit given to the Commercial banks were very encouraging.
Question 12: (a) What is incidence of taxes?
(b) Explain allY four principles of taxation.
Observation: The question was well attempted by the candidates. Most (l)' them provided the appropriate answers for the (a) and (b) parts of the question. IluIVCVCI", very few candidates only listed their points in the (b) part which obviously made them to score low marks.









No comments:
Post a Comment